บทความ
เนื้อหาบทความนี้ อ้างอิงจาก Guideline ของ International Association of Dental Traumatology (IADT) ปี 2020 ร่วมกับ Guideline ของ American Association of Endodontists (AAE) ปี 2013 และ 2014 และ European Society of Endodontology ปี 2021
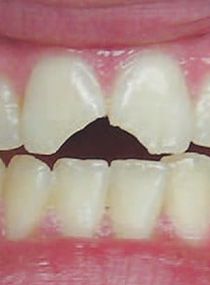
เมื่อเกิดการแตกของตัวฟัน สิ่งที่ทันตแพทย์ควรจะประเมินก่อนเพื่อช่วยวางแผนการรักษาคือ ฟันแตกหักถึงชั้นเนื้อฟันหรือไม่ ถึงเนื้อเยื่อในหรือไม่ ปลายรากฟันสร้างสมบูรณ์แล้วหรือไม่ และการบูรณะรอยแตกทำได้อย่างไร รวมถึงมีการบาดเจ็บแบบ luxation ร่วมด้วยหรือไม่ โดยมีแนวทางการประเมินฟันแตกและการรักษาแบ่งตามประเภทของ Crown fracture ดังนี้
1.) Enamel fracture
Clinical finding
ฟันไม่โยก และตอบสนองปกติต่อ pulp sensibility test, percussion & palpation test (ยกเว้นในกรณีที่มี luxation ร่วมด้วย) Radiographic finding: periapical 1 ภาพ ไม่พบความผิดปกติ
Treatment
ยึดติดชิ้นส่วนที่หักด้วย bonding resin หรืออุดฟันด้วย composite resin (CR) หรือกรอลบคม ติดตามผล pulp condition ที่ 6-8 สัปดาห์ และ 1 ปี
2.) Uncomplicated Enamel and Dentin fracture
Clinical and Radiographic finding
เหมือน enamel fracture มักไม่พบความผิดปกติ ยกเว้นมี luxation ร่วมด้วย
Treatment
เป้าหมายคือ ปกป้อง pulp และบูรณะฟันเพื่อการใช้งานและความสวยงาม
- ถ้าชิ้นฟันหักยังอยู่ ให้ทำการแช่ชิ้นฟันในน้ำ หรือน้ำเกลือ 20 นาที แล้วยึดติดด้วย bonding resin
- ถ้าไม่มีชิ้นฟัน ให้ทำการปกคลุมเนื้อฟันด้วย bonding agent+flowable CR หรือ Glassionomer cement (GI) ในกรณีที่เนื้อฟันเหลือหนาน้อยกว่า 0.5 mm (เห็นสีชมพูและไม่มีเลือดออก) ให้รองพื้นด้วย Ca(OH)2 lining และปิดทับด้วย GI
- รีบนัดผู้ป่วยกลับมาบูรณะเป็นวัสดุถาวร ติดตามผลที่ 6-8 สัปดาห์และ 1 ปี
3.) Complicated Enamel and Dentin fracture
Clinical and Radiographic finding
เหมือน enamel fracture มักไม่พบความผิดปกติ ยกเว้นมี luxation ร่วมด้วย
Treatment
- Immature tooth เป้าหมาย รักษา vital pulp ไว้ เพื่อให้รากเจริญต่อไป ถ้าจุดทะลุขนาดเล็ก และมาพบทันตแพทย์หลังบาดเจ็บไม่กี่ชั่วโมง สามารถทำ Direct pulp capping แต่หากจุดทะลุขนาดใหญ่ และมาหลายชั่วโมงหลังบาดเจ็บ แนะนำให้ทำ partial pulpotomy วัสดุ Capping ควรใช้ non staining calcium silicate cement หรือ non setting Ca(OH)2 และบูรณะฟันที่แตกด้วยการยึดติดชิ้นฟันที่แตก หรืออุดด้วย CR หรือ GI
- Mature tooth พิจารณาว่า ควรจะทำ Root canal treatment หรือ Vital pulp therapy ขึ้นกับการบูรณะฟัน ถ้าหากต้องทำ post and core ก็ต้องทำ Root canal treatment หากไม่ต้องทำ post and core ก็สามารถทำ pulp capping หรือ partial pulpotomy แบบฟัน immature ได้ อย่างไรก็ตามหากฟันได้รับบาดเจ็บแบบ luxation ร่วมด้วย จะมีโอกาสเกิด pulp necrosis มากขึ้น (ขึ้นกับความรุนแรงของ luxation ด้วย) ดังนั้นควรพิจารณาทำ Root canal treatment มากกว่าการรักษาแบบ vital pulp therapy
Follow up
- ตามระยะเวลาดังนี้ คือ 6-8 สัปดาห์ 3 เดือน 6 เดือน และ 1 ปี
- หากพบ pulp necrosis ให้รักษาคลองรากฟัน
4.) Crown and Root fracture
Clinical finding
ตอบสนองต่อ pulp sensibility test, +ve to percussion ชิ้นส่วนที่แตกโยก และควรประเมินว่ารอยแตกอยู่เหนือหรือใต้กระดูกเบ้าฟันเพราะมีผลต่อการบูรณะฟัน
Radiographic finding
ส่วนใหญ่ในภาพรังสีจะไม่สามารถเห็นได้ว่าแตกลงไปถึงแค่ไหน ควรถ่ายภาพรังสี periapical film ตรง 1 ภาพ และอีก 2 ภาพที่เปลี่ยนมุมแนวนอนหรือแนวดิ่ง และ Occlusal radiograph อาจถ่าย CBCT เพื่อช่วยให้มองเห็นตำแหน่ง ที่แตกเทียบกับขอบกระดูก ประเมินสัดส่วนตัวฟันและรากได้ เพื่อช่วยวางแผนการรักษา
Treatment
จนกว่าจะวางแผนการรักษาเสร็จสิ้น ควรพยายามทำการยึดชิ้นส่วนที่ขยับกับฟันข้างเคียง หรือส่วนที่ไม่ขยับของฟันซี่นั้นไว้ก่อนและประเมินว่ามีจุดทะลุเนื้อเยื่อในหรือไม่
Follow up (ในกรณีเก็บฟันไว้)
1 สัปดาห์ 6-8 สัปดาห์ 3 เดือน 6 เดือน 1 ปี และทุกๆปีไปถึง 5 ปี